

You can change the titles and labels of a scatter plot with the TITLE statement, the XAXIS statement, and the YAXIS statement.
Scatterplot matrix how to#
In this section, we explain how to change the titles of a scatter plot. Moreover, the labels (or titles) of the x-axis and y-axis are, by default, the labels of the corresponding variables. How to Change the Titles of a Scatter Plotīy default, a scatter plot in SAS doesn’t have a title. If you want to legend to be a vertical list instead of a horizontal list (default), then you use the across=1 option.Īll 3 arguments are optional and must therefore be placed at the end of the KEYLEGEND statement after a forward slash. With this option you define the number of columns of the legend. For example, to place the legend in the upper left corner, you use the abbreviation of North-West (NE). With this option you define the position of the legend. With this option you specify if SAS places the legend inside or outside the scatterplot.
Scatterplot matrix code#
In the SAS code below we create a legend with 3 of the most common optional arguments, namely: You can add additional arguments to control the legend’s appearance. By adding this statement, SAS will automatically create a legend. In SAS, you can add a legend to a scatter plot with the KEYLEGEND statement. A legend is especially useful if you create a grouped scatter plot. The SAS code in the example below generates a basic scatter plot and shows the relationship between the variables SepalLength and PetalLength.Ī good practice of visualizing data is to add titles and legends to your plots. You finish and execute the code of the SGPLOT procedure with the RUN statement. For example, you can add a legend, a regression line, or a title. You can add extra statements to the SGPLOT procedure to enhance the scatter plot. Optionally, add statements to enhance the scatter plot.You can add additional options to, for example, create a grouped scatter plot. This statement starts with the scatter keyword, followed by the variable for the x-axis, and the variable for the y-axis. You create the actual scatter plot with the SCATTER statement. This option starts with the data keyword, followed by an equal sign and the name of your dataset. You define the name of the input data with the data=-option. You start the SGPLOT procedure with the PROC SGPLOT keywords.

Set.These are the steps to create a scatter plot in SAS: Using these strategies, here is some example R code and the plots made: # the alpha argument in rgb() lets you set the transparencyĬols2 = c(rgb(red=255, green=0, blue=0, alpha=50, maxColorValue=255),
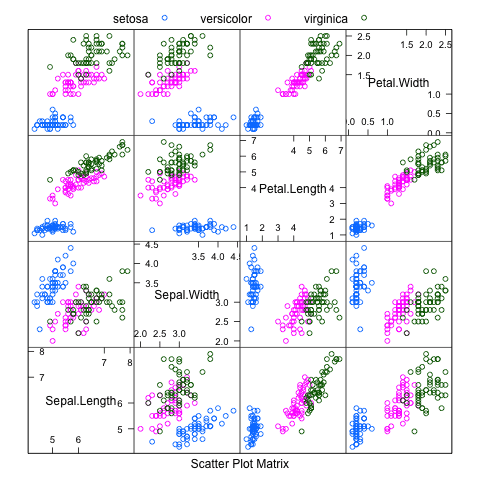
There are algorithms for determining an optimal amount, but since your data come in whole units from one to ten, $.5$ seems like a good choice.
Scatterplot matrix plus#
The noise is taken from a uniform distribution centered on your value plus or minus some small amount. Jittering means adding a small amount of noise to the values in your dataset. There are several tricks to help you deal with this. Thus, you cannot see how many points are at each location. Since you have a lot of data at discrete points in the space, they end up stacking on top of each other. You just need to make multiple plots, one for each block. Notice that you can break a scatterplot matrix into smaller blocks of four or five (a number that is usefully visualizable). Also, although you do want to see every combination, you don't have to plot them all together. The thing to notice is that many plots are duplicated, which wastes space.
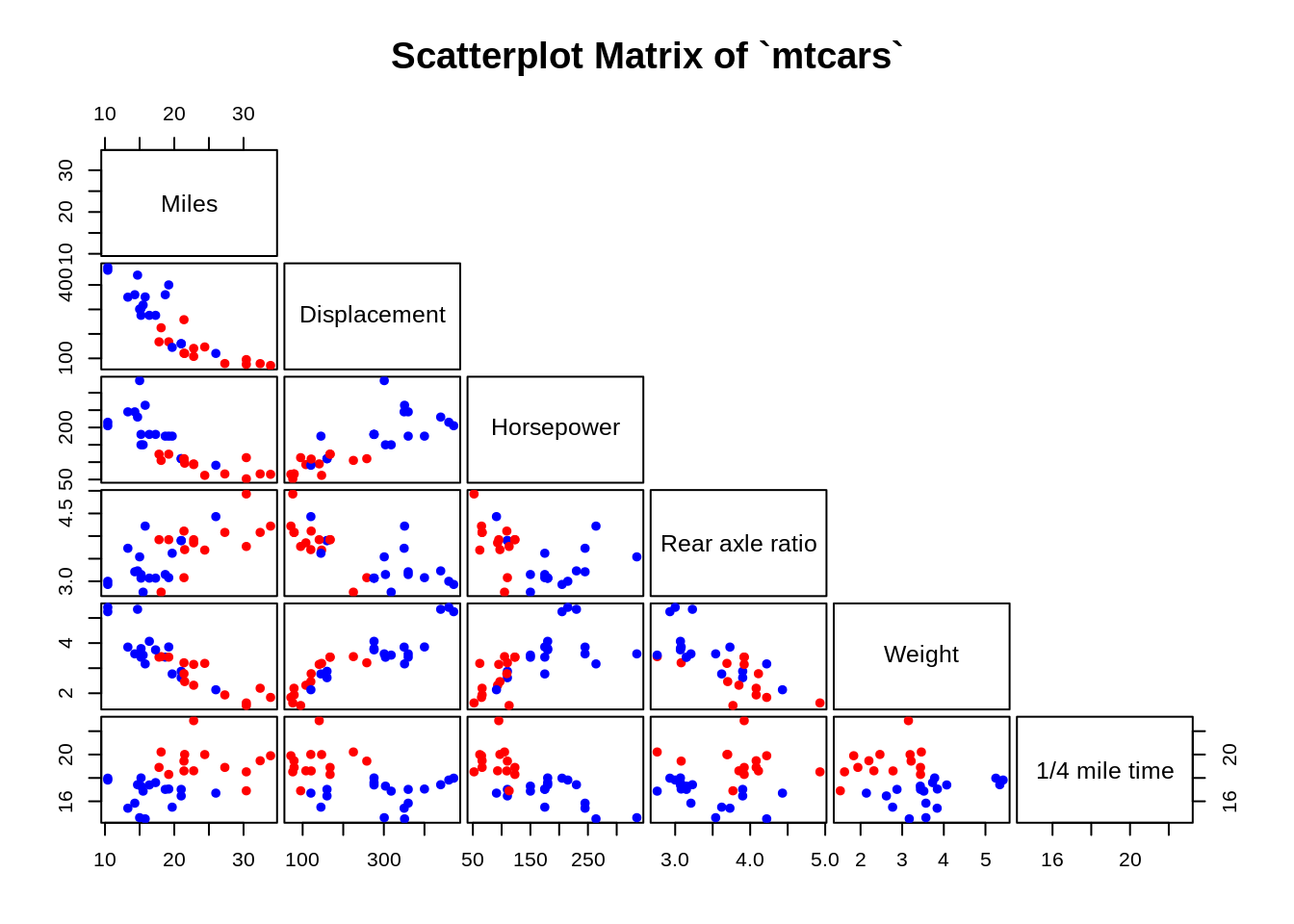
When you have lots of variables in a scatterplot matrix, each plot becomes too small to be useful. You have too many variables displayed together. There are a number of issues that make it difficult or impossible to extract any usable information from your scatterplot matrix.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
